Effect of Straw Returning on Soil Nutrient Content in Farmland
The continuous promotion of high-yield, high-quality varieties of crops and the increase of the crop multiple cropping index require not only a higher soil fertility load, but also a higher level of fertility. Organic manure has the special function of fertilizing the soil and regulating soil nutrients. However, as the amount of chemical fertilizers continues to increase, the application of organic manure becomes less and less. As the main source of organic manure, crop stalks directly returning to the field to increase soil organic matter have become inevitable. For this reason, the author conducted a localization experiment of organic and inorganic fertilizers in Guangde County, Anhui Province, from 1997 to 2001, and studied the effect of increasing crop yield and fertilizing soil after crop straw returning.
1 Test materials and methods The test site is located in paddy field, Yangshen Township, Guangde County, Anhui Province. A total of five tests were performed: single fertilizer application; chemical fertilizer + rice straw-1; chemical fertilizer + rice straw-2; chemical fertilizer + wheat straw; The experimental plot area is 24m2, 3 repetitions, completely random design. Straw-1, wheatgrass, and rape straw were applied at a rate of 1 500 kg/hO and straw was applied at a rate of 3 000 kg/hO. The same amount of chemical fertilizers was used for the 5 treatments, ie 150 kg/hO of pure N fertilizer, P2O545 kg/hO, and K2O 90 kg/hO. Urea for nitrogen fertilizer, calcium superphosphate for phosphate fertilizer, and potassium chloride for potassium fertilizer. All phosphate fertilizers, potash fertilizers, rice straw, wheat straw, rape straw and 50% nitrogen fertilizer were used as base fertilizers, and the remaining 50% nitrogen fertilizer was used as top dressing. The experiment was carried out continuously for 4 years. When the crops were harvested in each season, the plant samples were collected from each plot and the plant morphology and yield composition were observed. The yield of each plot was actually collected.
2 Test results and analysis 2.1 Effect of different treatments on soil fertility As an organic fertilizer, straw has a slow and long-lasting effect, and in addition to providing nutrients for crops, it also provides necessary energy and nutrients for the life activities of soil microorganisms. . Soil organic matter is an important indicator to measure soil fertility. The most fundamental role of straw returning is to increase soil organic matter content. Table 1 shows the data of soil nutrient content measured by the soil nutrient tester on soil samples. It can be seen that the organic matter content increased by 17.5% to 28.7% after rice straw was returned to the field, and the organic matter content increased by 17.5 after the rape straw was returned to the field. %; After wheatgrass returned to field, organic matter content increased by 14.0%. With the increase of organic matter, the nitrogen nutrients in the soil can be significantly improved after mineralization. Compared with the control, the soil total nitrogen content increased by 28.5%-40.1% after returning rice straw, the alkaline nitrogen content increased by 13.2%-30.8%, and the soil total nitrogen content increased by 5.5% after wheat straw returning. The content increased by 14.3%; the soil total nitrogen content increased by 26.7% and the alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen content increased by 14.3% after the rape stalks were returned to the field. Straw returning also facilitates the accumulation and improvement of soil available potassium.
After rice straw returned to field, the content of available potassium increased by 12.9%~21.0%. After wheat straw returned to field, the content of available potassium increased by 12.1%. After the rape straw was returned to field, the content of available potassium increased by 4.8%. Straw returned to the field with the best effect of rice straw, and the greater the amount of rice straw returned, the greater the increase in soil nutrients.
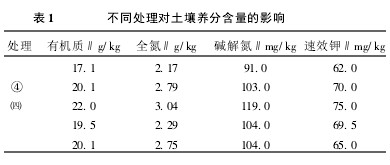
Table 1 Effect of different treatments on soil nutrient content 2.2 Effect of different treatments on crop yield After crop straws return to farmland, soil nutrient content increases, especially soil available nutrient content and microbial biomass increase more, and at the same time improve soil physical properties. It has a significant effect on the improvement of crop yield. See Table 2 for the average yield of rapeseed and rice treated differently in the 4 seasons and 8 seasons (1997-2001). The results showed that the average yield of rapeseed returning rape was 148~184 kg/hm2, and the increase rate was 8.56%~10.64%. The yield of rice increased by 430~490 kg/hm2 and the yield increased by 6.89%~7.85%. Rape stalk and wheatgrass returning rape respectively increased the yield by 84 and 48kg/hm2, the yield increase was 4.86% and 2.78%, respectively; rice yield increased by 354 and 312 kg/hm2 respectively, and the yield increase was 5.67% and 5.00%, respectively. It can be seen that the most significant increase in straw yield is the return of crops, and the crop yield increases with the increase in the amount of straw.
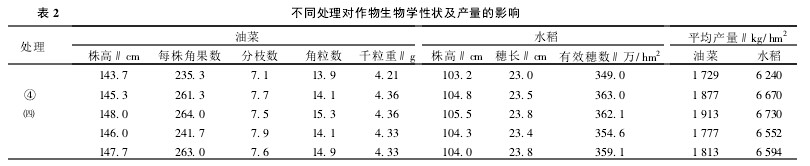
Table 2 Effects of different treatments on crop biological characteristics and yields 2.3 Effects of different treatments on biological characteristics of crops After straws are returned to the field, straws cover the surface of the soil, so that the soil can avoid direct sunlight and rain erosion, and moisture does not easily evaporate. And loss, nutrient loss is not easy, can be fully absorbed and utilized by crops, crop vegetative growth accelerated. As can be seen from Table 2, the plant height of rice straw increased by 1.6 to 3.0 cm; the plant height of rice increased by 1.6 to 3.0 cm. The plant heights of rapeseed stalk returning and wheat straw returning were respectively increased by 2.3 and 4.0 cm, and the plant height of rice increased by 1.1 and 0.8 cm, respectively. Good vegetative growth lays the foundation for reproductive growth. Crop stalks are rich in N, P, and K nutrients. After rot, providing necessary nutrients for crops, especially rich potassium nutrients, has a significant effect on promoting the reproductive growth of crops. Potassium nutrients also have a strong stalk effect, so that rape can grow healthily and increase branching. As can be seen from Table 2, the number of pods per straw increased by 26.0 to 28.7, the number of branches increased by 0.4 to 0.6, the number of pods increased by 0.2 to 1.4, and the grain weight increased by 0.15 g; Spike length increased by 0.5 to 0.8 cm, and effective panicles increased by 134,000 to 140,000. The number of pods per rapeseed stalk returning and wheat straw returning rape increased by 27.7 and 6.4, respectively. The number of branches per plant increased by 0.5 and 0.8, and the number of pods increased by 1.0 and 0.2, respectively. Thousand kernel weight increased. 0.11g; rice ear length increased by 0.8 and 0.4 cm, effective panicles increased by 111,000 and 56,000/hO, respectively.
3 Test conclusions 3.1 The fertility test results of straw returned to field showed that the application of chemical fertilizer with straw on acidic red and yellow soil increased soil organic matter content by 14.0%~28.7% compared with single fertilizer application. Due to the increase of soil organic matter, it promotes the enrichment and coordination of nutrients in the soil. Compared with single fertilization, straw returning increased the total nitrogen content in soil by 5.5% to 40.1%, alkalized nitrogen increased by 13.2% to 30.8%, and effective potassium increased by 4.8% to 21.0%. The return of crop straw to the soil can increase the soil nutrient content, and the best effect is straw returning, and the increase of soil nutrient increases with the increase of straw returning amount.
3.2 Returning Straw to Crops to Increase Crop Yield The return of straw to the field has a greater effect on the increase of crop yield. The average yield of rapeseed was 48~184 kg/hO, the increase rate was 2.78% ~ 10.64%, and the average yield of rice was 312~490kg/hO, an increase of 5.00%~7.85%. The highest straw yield was returned, straw> rape straw> wheat straw> single fertilizer, and the crop yield increased with the increase of straw usage.
Heavy duty rack is commonly and widely used for industrial storage, including Selective Pallet Rack, VNA rack, push back rack, drive-in rack, gravity oallet flow rack and so on.
Heavy Duty Rack is a type of rack that is more durable and robust than a regular rack, and is typically used for heavier and longer goods, capable of carrying a heavier load while keeping the goods secure. Heavy Duty Rack is composed of a very sturdy rack structure that can support loads of goods, and is made of durable materials, able to withstand heavier weights. Heavy Duty Racks can be adjusted with different layers height based on the requirements, for precise picking and distribution.
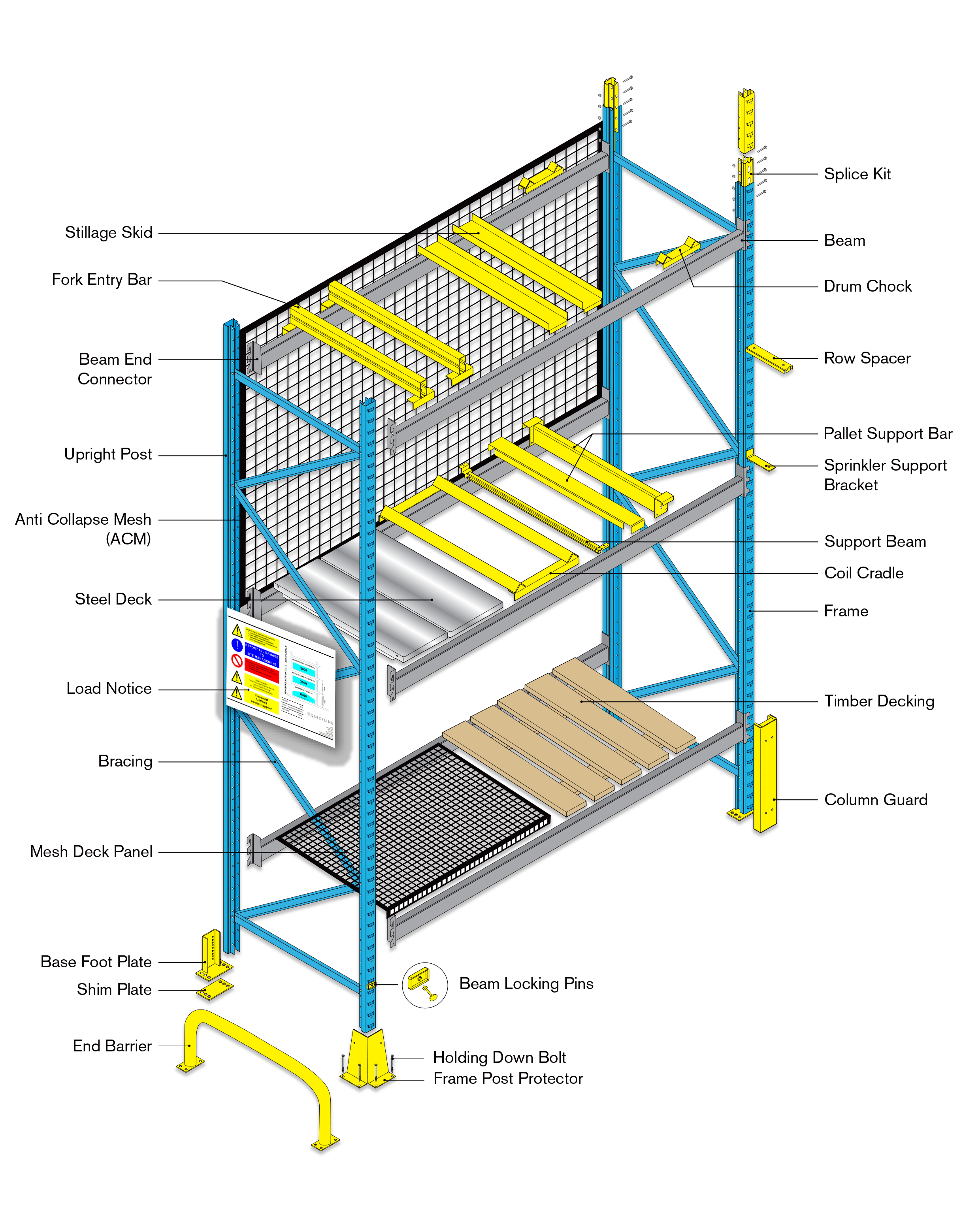
Heavy Duty Rack,Heavy Duty Shelving,Heavy Duty Rack Shelf,Heavy Duty Garage Shelving
Nanjing Chinylion Metal Products Co., Ltd , https://www.clrack.com
