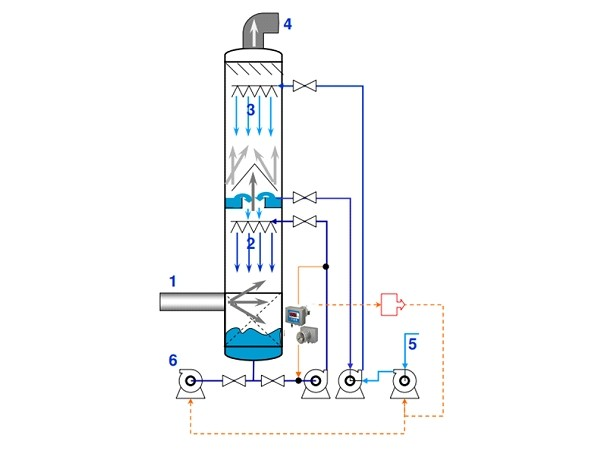
DMF/DMAC/Ammonia recycle application
In addition to its industrial uses, phosphorus pentasulfide has also been used in the laboratory for the synthesis of various organic compounds, including thioesters, thioamides, and thioethers. It is typically used as a reagent in these reactions, as it can convert carboxylic acids and other functional groups into their corresponding thio derivatives.
Phosphorus pentasulfide (P2S5) is a chemical compound composed of two phosphorus atoms and five sulfur atoms. It is a yellowish-green solid that is insoluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents.
Phosphorus pentasulfide is commonly used in organic synthesis as a reagent for the conversion of alcohols to thiols and thioesters. It is also used in the production of insecticides, fungicides, and herbicides.
Phosphorus pentasulfide is a highly reactive and flammable compound that can pose a significant health hazard if not handled properly. It can cause severe irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system, and is considered a potential carcinogen. Proper protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn when handling this compound.
Phosphorus pentasulfide (P2S5) is a highly reactive and dangerous chemical compound that is commonly used in the production of pesticides, lubricants, and other industrial chemicals. It is a yellowish solid that can be easily ignited and releases toxic fumes when exposed to air or water.
Exposure to phosphorus pentasulfide can cause severe respiratory and skin irritation, as well as eye damage. Inhalation of the fumes can lead to coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, while skin contact can cause burns, blisters, and chemical burns.
Phosphorus pentasulfide is also highly flammable and can ignite spontaneously when exposed to air or moisture. It reacts violently with water, releasing toxic hydrogen sulfide gas, which can cause respiratory failure and even death.
Due to its highly reactive nature and potential health hazards, phosphorus pentasulfide should only be handled by trained professionals in a controlled environment with appropriate safety measures in place.
Chemical Phosphorus pentasulfide with CAS 1314-80-3,Phosphorus Pentasulfide Cas 1314-80-3,Phosphorus Pentasulfide Hazardous Chemical,Dangerous Chemical Phosphoric Sulfide
Sichuan Jinhe Qihang Co,. Ltd. , https://www.jinhechemicals.com
